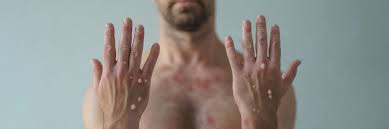
In the face of a health crisis such as the recent outbreak of the MPOX virus, behavioral changes and vaccine inequities play a crucial role in determining the success of the response efforts. Understanding the interplay between human behavior and access to vaccines is essential for public health officials to effectively curb the spread of the virus and mitigate its impact on society.
Behavioral Changes in Response to the MPOX Outbreak
One of the key factors influencing the spread of the MPOX virus is human behavior. In the early stages of the outbreak, behavioral changes can have a significant impact on the rate of transmission. For example, practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and covering coughs and sneezes, can help prevent the spread of the virus.
Furthermore, adopting social distancing measures, such as avoiding large gatherings and staying at home when feeling unwell, can also help slow down the transmission of the virus. These behavioral changes are especially important in the absence of a widely available vaccine, as they can help reduce the burden on healthcare systems and protect vulnerable populations.
Vaccine Inequities in the MPOX Outbreak Response
Access to vaccines is another critical aspect of the response to the MPOX outbreak. Inequities in vaccine distribution can undermine efforts to control the spread of the virus and exacerbate health disparities within communities. It is important for public health officials to ensure that vaccines are distributed equitably, taking into account factors such as geographic location, socioeconomic status, and access to healthcare services.
Addressing vaccine inequities requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes establishing targeted vaccination campaigns in underserved communities, providing resources and support for those who may face barriers to accessing vaccines, and ensuring that healthcare providers are equipped to administer vaccines effectively and efficiently.
In addition, public health officials must work to build trust and confidence in the vaccine among the general population. Misinformation and mistrust can hinder vaccination efforts, particularly in communities that have historically faced discrimination and marginalization. Engaging with community leaders, promoting transparent communication, and addressing concerns and misconceptions about the vaccine are crucial steps in building vaccine confidence and increasing vaccination rates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, behavioral changes and vaccine inequities are key considerations in the response to the MPOX outbreak. By understanding the impact of human behavior on the spread of the virus and addressing inequities in vaccine distribution, public health officials can improve the effectiveness of their response efforts and protect the health and well-being of society as a whole. By implementing targeted interventions, promoting equitable access to vaccines, and building trust and confidence in the vaccine, we can work together to control the spread of the MPOX virus and minimize its impact on communities around the world.